Knee osteoarthritis is a specific disease that has a destructive effect on the cartilage of the knee joint.
When such a disease occurs, doctors observe serious disturbances in the processes of blood circulation in the bone vessels, as a result of which deformation and destruction of cartilage tissue occurs, a person experiences severe pain that limits any movement of the legs and knees, observes swelling and changes in the appearance of the knees.
To prevent the development of serious consequences of gonarthrosis (deformation of the limb and ankylosis - immobilization of the joint), when only joint replacement surgery can help the patient, the disease must be promptly identified and treated.In addition, do not self-treat with folk methods and advertised means, but under the supervision of qualified doctors.
What are the reasons?
The mechanisms of arthrosis in medicine are usually divided into:
- Primary- which occurs in old age from the natural aging of body tissues and against the background of some factors that provoke this disease, such as obesity (10% of cases), heredity and increased stress throughout life.
- Secondary- represents 30% of all cases of arthrosis of the knee joint;usually occurs after an injury, fracture of the tibia, torn ligaments or damage to the meniscus.In addition, with such arthrosis of the knee joint, the symptoms of the disease in most cases appear after 3-4 years, but after a serious injury it is possible even after 2-3 months.
In 50-60% of cases, the cause of arthrosis of the knee joint is a spasm of the muscles on the front surface of the thigh.
What happens to the knee joint in osteoarthritis?
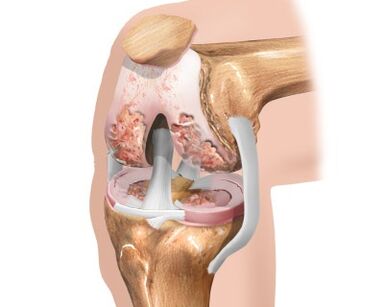
With excessive regular loads, genetic predisposition, metabolic disorders in the body, prolonged muscle spasms and injuries, the knee cartilage loses its smoothness and begins to thin.The soft sliding of the articular bones is replaced by strong friction and the first degree of gonarthrosis develops, in which the cartilage loses its shock-absorbing properties.
The degradation process continues to progress and poor shock absorption leads to flattening of the bone surfaces with the formation of osteophytes in the form of bone growths.In this case, the disease already has the second degree and is accompanied by degeneration of the synovial membrane and joint capsule.The lack of pumping and movement atrophies the structure of the knee joint, the consistency of the knee fluid becomes more viscous, the process of cartilage nutrition is disturbed, which leads to an even greater deterioration of the patient's condition.
The thinning of the cartilage leads to a reduction in the distance between the articular bones by up to 80%.During walking, due to abnormal friction and lack of a shock absorber, the destructive processes in the joint rapidly increase, which quickly leads to the development of third degree arthrosis with pronounced symptoms:
- Pain when moving, especially going up or down stairs.
- Pain both during exercise and at rest, morning stiffness.
- The patient begins to limp, trying to spare the diseased joint.
- Severe cases of the disease require the use of crutches or a cane.
The third degree of arthrosis of the knee joint is characterized by an almost complete absence of cartilage tissue, which leads to a reduction in the mobility of the joints to a minimum.Therefore, no magical methods, supermedicines or ointments can restore the worn cartilage tissue, and given the degree of bone deformation, the normal functioning of the joint is impossible.In this case, only surgery can help.
Stages of arthrosis
As arthrosis progresses, the following stages or degrees are distinguished:
- The initial stage or stage 1 is often called compensated, since there are still no pronounced clinical signs of pathology.The patient may feel discomfort in the knees after physical activity, which quickly disappears after rest;the joints are still fully functional.
- In arthrosis of the 2nd degree, subcompensated, the symptoms of the disease intensify.A pronounced pain syndrome is formed, which, however, is relieved by anesthetic ointments and gels used locally.Motor activity is impaired and joint instability appears.In the majority of cases, patients turn to doctors at this stage.
- The 3rd degree, decompensated, can also be called deforming.The knee joint is twisted, unstable, immobile and completely non-functional.The pain syndrome is permanent and requires serious medical intervention.To relieve the joint and move, a person needs a cane.
Symptoms and first signs
Depending on the severity of the symptoms, the development of the disease is divided into 3 stages.Symptoms of the early development of gonarthrosis are very diverse and not specific.
At the first stage of the pathology, the following signs are possible:
- knee pain when squatting or walking up stairs;
- pain in the joint after prolonged exertion or cooling;
- the knee may hurt at the end of the day or in the morning;
- stiffness and soreness in the morning disappear after daily work.
Subsequently, symptoms characteristic of stages 2 and 3 appear (in ascending order):
- the pain becomes sharp and prolonged;
- swelling in the joint area;
- fluid may appear in the joint;
- between the joint surfaces, it is possible to pinch particles of cartilage, meniscus, synovial villi, as a result of which a sharp immobility occurs (it can also pass suddenly);
- it is difficult to step on your feet;
- joint immobility develops.
Consequences
If left untreated, the following complications of knee arthrosis may develop:
- Joint deformity.In fact, the deformation of the joint is not a complication, but the last stage of the disease.
- Infection in the joint.Infection usually occurs due to microtrauma.They can be considered small cracks in the cartilage tissue.Pathogenic microorganisms are introduced into the joint through the flow of blood or lymph from other areas.This often happens after infectious diseases.
- Dislocations and fractures.These complications are explained by knee joint dysfunction.In arthrosis, there is no uniform distribution of the load from the femur to the bones of the lower leg.The ligaments that normally strengthen the joint also weaken.Therefore, at a certain point (even with normal walking) the bones of the lower leg can be subjected to excessive stress, which will lead to a fracture or luxation.To avoid this, people with severe structural and functional disabilities in the knee joint must move with the help of a crutch or a cane.
- Ankylosis.Ankylosis is the fusion of two bones where a joint once existed.This complication is perhaps the most severe, as the joint simply disappears.The tibia and femur gradually fuse and the tibia is fixed in one position.Movement, of course, is impossible.
Diagnosis
To diagnose gonarthrosis, use:
- blood tests (general and biochemical);
- radiography;
- arthroscopy;
- ultrasound;
- MRI.
The most important diagnostic method for confirming the diagnosis of gonarthrosis is radiography.Although it is not possible to examine the initial stages of the disease and the condition of the cartilage tissue on X-rays, however, bone changes in stages 2 and 3 are clearly visible.this:
- narrow joint space;
- marginal spines located along the contour of the bones, the edges of the patella - osteophytes;
- changes in the periosteum;
- change in the height of one of the condyles and others.
However, the changes can be examined in more detail with the help of arthroscopy.
Ultrasound and MRI help detect changes in the soft tissues of the knee joint during early arthrosis.These methods also give a good indication of the condition of cartilage tissue, synovium and fluid.
How to treat arthrosis?
Treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint is long and sometimes painful.The duration is due to the fact that once the disease has manifested itself, it will constantly remind of itself as long as a person lives.
Therefore, in order to properly treat gonarthrosis, a fairly strong financial foundation and discipline is required.An important role is played by how seriously the patient takes the treatment, because often, in order to reduce the frequency of exacerbations of the disease, the patient is forced to change his daily activities, his favorite profession, engage in joint development, give up smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
There are three main stages in the treatment of deforming arthrosis of the knee joint.
The first stage of treatment includes:
- informing patients about the nature of their disease, risk factors and secondary prevention measures;
- daily gymnastics with stretching elements;
- contrast shower;
- swimming in a pool 2-3 times a week;
- weight loss.
The second stage of treatment includes:
- external fixation of the joint using calipers, bandages, elastic bandages and orthoses;
- the use of ointments and creams based on nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve inflammation and pain;
- the use of drugs from the group of chondroprotectors to reduce the rate of cartilage destruction.
The third stage of treatment includes:
- course use of NSAIDs orally;
- intra-articular injections with hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- additional use of drugs with a marked analgesic effect;
- surgical replacement of a diseased joint with an implant.
Along with drug treatment, modern medicine uses methods such as:
- Kinesitherapy.In this case, the treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint is carried out with the help of special exercises.The load is selected individually depending on the degree of development of the disease and the physical fitness of the patient.
- Ozone therapy.This is an impact on a sick knee joint with the help of ozone.With this method of physiotherapy treatment, the substance can be administered by injection or used externally.
- food supplement.Biologically active supplements are a worthy alternative to other drugs.
- Homeopathy.This includes taking medication in small doses.The course of treatment lasts only a few weeks, but during this time, provided that the drugs are correctly selected, blood circulation and normal nutrition of cartilage tissue cells are completely restored.
- Exercisesallow you to improve blood circulation in the knee joint, restore the elasticity of the ligaments, improve the nutrition of cartilage tissue cells and promote its recovery.
Drug treatment
All drugs used in the treatment of gonarthrosis can be divided into those that help eliminate the main symptoms of the disease and those that restore the function of the knee joint and prevent the progression of the pathology.The first type of drugs includes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and hormonal drugs.The second group includes chondroprotectors and hyaluronic acid.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Drug treatment of arthrosis begins with pain relief.They are the ones that cause the greatest moral and physical suffering to patients and lead to loss of working capacity.Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) have worked well among pain relievers.
Medicines can be used in two ways - topically or orally (in tablets).Topical treatments (preferred) often include patches, ointments, or gels.The analgesic effect, as a rule, occurs in 3-4 days, and its maximum develops in 7-10 days.
The course of treatment with non-steroidal drugs should be limited to 10-14 days.NSAIDs have a limited scope of application and are used with great caution in the treatment of elderly patients.
Hormonal drugs
In cases where NSAID treatment is not sufficient and the disease continues to progress, the doctor may prescribe hormone injections.They belong to the means of "heavy artillery" and help to quickly eliminate pain, relieve inflammation and swelling of the surrounding tissues.
Due to the large number of side effects, hormonal drugs are prescribed in short courses, only in the acute period of the disease, when the inflammatory fluid accumulates in the joint cavity.The drug is applied into the joint space no more than once every 10 days.
Chondroprotectors
To prevent further destruction of the cartilage surfaces of the joint, chondroprotectors are prescribed.
These medications also help reduce pain and signs of inflammation in the surrounding soft tissue.In addition, chondroprotectors slow down the destruction of joint tissues and stabilize the disease due to their shock-absorbing and lubricating functions.Chondroprotectors improve cartilage nutrition, normalize the composition and properties of the intra-articular fluid and protect pain receptors from excessive irritation.
Hyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid is called a fluid prosthesis from intra-articular fluid.In its properties, it is similar to the natural synovial (intra-articular) fluid, which nourishes the cartilage tissue and softens the knee joint during movements.
Hyaluronic acid preparations are injected into the joint, thus creating a thin protective film that prevents the cartilage surfaces from rubbing against each other.Injections are performed only after passing the acute phase of the disease.
Exercise therapy and exercises for osteoarthritis
Physical exercises help to restore joint function and strengthen them.They must be performed slowly and carefully so as not to get sprains and not to exceed the permissible load.
The following exercises are considered the most effective:
- Slowly raise your standing legs one at a time while lying on your stomach.This exercise uses the thigh and calf muscles.The load must not be allowed to be transferred to the back.You shouldn't raise your legs too high either.The main thing is to tense your muscles at the top point;
- This exercise is similar to the first, only now you need to raise your leg with a bent knee.At the top point, the thigh muscles should be additionally strained.The exercise should be performed an equal number of times on each leg;
- Lie on the floor (on your stomach), lift your straight legs up, then spread them apart and bring them together.This exercise requires strong, trained abdominal muscles, so it is not suitable for all patients.In addition, its implementation can increase blood pressure.For patients suffering from hypertension or other diseases of the cardiovascular system, it is better to avoid it;
- To perform the next exercise, you need to lie on your side, bend your leg on the floor at the knee, and slowly raise the other leg and hold it at the top point.It is important that the angle when performing each leg is the same;
- You will need a chair for this exercise.Sitting on it, the legs are straightened one by one, raised and held for the maximum possible time in an upright position;
- It is helpful to rise on your toes while holding the back of a chair or bed.As with other exercises, you need to stay at the top point for a few seconds and additionally strain the leg muscles;
- Smooth movement from toes to heels allows you to activate blood circulation in the lower limbs.Such movements should be performed sequentially: while one leg rests on the toe, the other on the heel and vice versa.All movements should be smooth;
- Leaning against the back of a chair or bed, stand on your heels for a minute, lifting your toes up.If you cannot stand in this position for the specified time, you should start with less, gradually increasing it;
- A massage that is performed in a standing position.The legs should be rubbed with vigorous movements directed from the knee up to the thigh.It is necessary to finish the massage by stroking the skin.
The doctor will conduct several sessions in the office and show basic techniques so that the patient can massage the problematic knee himself.Competent actions improve the condition of the damaged area.
Massage and self-massage
Self-massage with your palm, the edge of your palm, your fingertips, or your fist.Carefully act on the painful knee, maintain strong pressure on the affected area: strong tapping, blows, active kneading of tissues often worsen the condition.
Basic techniques:
- the first stage is light stroking in a clockwise direction, the second stage is counterclockwise circular movements;
- Press one palm to the sore knee, lightly pat it with the fingertips of the other hand;
- maintain the initial position of the palm, tapping not with fingers, but with the edge of the palm;
- lightly stroke the knee in a circle, gradually increase the pressure (but moderately);
- During the therapy, massage the affected area twice a day for 10-15 minutes.For preventive purposes, it is enough to do a light massage once every 7 days.
Before the procedure, apply ointment or gel with an anti-inflammatory effect to the affected knee.
Physiotherapy treatment
All physiotherapy methods can be divided into several groups:
- Pain reduction;
- Reducing inflammation;
- Restoring nutrition to the joint and accelerating the recovery of joint function.
A doctor can determine what type of treatment a patient needs based on existing symptoms and co-morbidities.
Surgery for arthrosis
Surgical treatment refers to radical methods that partially or completely restore the functioning of the knee joint.Surgical treatment methods differ from each other in the degree of intervention in the affected joint.
- Arthroscopyrefers to the most gentle methods of surgical treatment.This technique is less traumatic and can be used as a therapeutic measure even in the early stages of arthrosis.Its main purpose is to prolong the life of the damaged joint.Arthroscopy is performed using an endoscope - a flexible probe with a camera at the end.Small incisions are made in the knee joint through which an endoscope and auxiliary instruments are inserted.During the operation, the damaged areas of the tissue that cause pain are removed.The operation is best suited for young people and can be repeated several times if necessary.
- Endoprostheticsrefers to the most radical surgical techniques.In this case, the full restoration of the joint function is achieved by replacing the entire knee joint or part of it with an implant.This method is the best alternative to the previously existing technique - arthrodesis (complete immobilization of the damaged joint).Currently, endoprosthesis provides up to 90% positive results and significantly improves the quality of life of patients.
- OsteotomyIt is used when significant deformations have developed in the joint and the function of the joint is significantly impaired.Osteotomy involves creating an artificial bone fracture at a pre-planned location.Subsequently, the pieces of bone are aligned in the correct, physiological position and allowed to grow together.Sometimes during the operation, artificial fixators of bone fragments can be used, which contribute to a more stable position of the bone.
People's funds
Traditional medicine will also help you.The use of various lotions to relieve swelling and pain has long been practiced by many patients.Here are some useful recipes:
- Burdock leaves.Take 5 burdock leaves and hold them over boiling water to infuse.Lubricate the sore knee with vegetable oil and apply steamed leaves.Wrap your leg in cling film and a warm scarf.Leave the lotion on for a few hours.
- Cabbage leaf lotion.It is made from fresh cabbage leaves soaked in May honey and applied to the feet.The therapeutic effect is enhanced by insulation from woolen fabric or plastic film.This product is suitable for people of all age groups.
- Eggshells, kefir.Grind the shells of 2 eggs and mix with 1 spoon of kefir.Apply the mixture to the knee, wrap it with a towel and cling film and lie under a blanket.Leave it like this for several hours, then rinse the composition with water.This treatment can be used daily.
- Horseradish compress.According to this folk recipe, in order to enhance the healing properties of horseradish, it is recommended to first crush and boil it.It should then be applied to the affected area.
- Turpentine– an excellent warming agent for painful joints.The knee is smeared with turpentine before going to bed and tied with a woolen scarf.Already after the first procedure, the patient experiences significant relief.The course of treatment is chosen individually for each person.
diet
The therapeutic diet includes avoiding or minimal consumption of canned, smoked and fried foods (to suppress appetite).To restore the damaged cartilage, it is necessary to provide the body with complex carbohydrates (porridge, whole grain products).Juices (carrot, beetroot, apple) should also be included in the diet.They will remove toxins from the body and reduce the impact of inflammatory processes.
The diet should include fish and aspic, which act as a type of chondroprotector and help create new cartilage.It is worth remembering that you cannot prescribe a diet for yourself - only a nutritionist (diet specialist) can choose the best option.
Sample menu:
- Breakfast: oatmeal with water without oil or sugar, fruit juice, boiled egg;
- Second breakfast: a glass of low-fat natural yogurt;
- Lunch: steamed meat or fish, stewed vegetables, tea without sugar;
- Afternoon snack: cottage cheese casserole with nuts, a glass of fruit juice;
- Dinner: vegetable salad, apple, tea without sugar;
- Second dinner: a glass of low-fat kefir.
Prevention
Prevention of joint diseases:
- dose the load on your legs during active sports;
- create a diet that includes foods and dishes containing calcium, magnesium, gelatin;
- if the work involves lifting or moving heavy objects, observe safety rules and do not carry loads exceeding a certain limit;
- Do regular self-massage to prevent arthrosis, especially with constant stress on the feet;
- eat right, limit "harmful" foods;
- body weight control (overweight means additional stress on the joints);
- Have regular check-ups and treat acute and chronic illnesses.
Forecast
Provided that arthrosis of the knee joint is diagnosed in the early stages, the cause of the pathological process is eliminated and adequate treatment is carried out, the prognosis is favorable.The proposed therapy makes it possible to achieve long-term remission, but the treatment is usually lifelong.
In the absence of the necessary treatment, as well as when the patient does not follow the doctor's prescriptions, arthrosis of the knee joint becomes a cause of disability.


















